Anti-PCNA antibody[STJ96933]
Product nameAnti-PCNA antibodyShort DescriptionMouse monoclonal against PCNADescriptionPCNA is a protein encoded by the PCNA
| Product name | Anti-PCNA antibodySTJ96933] |
|---|---|
| Short Description | Mouse monoclonal against PCNA |
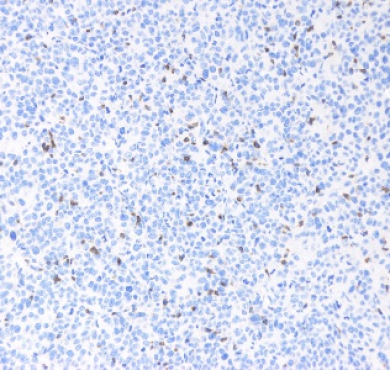
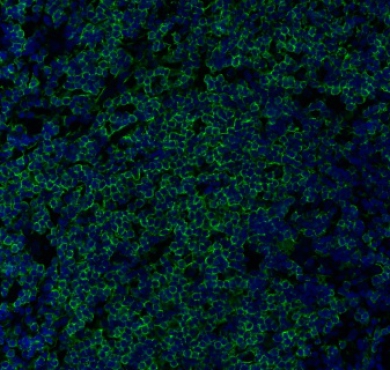
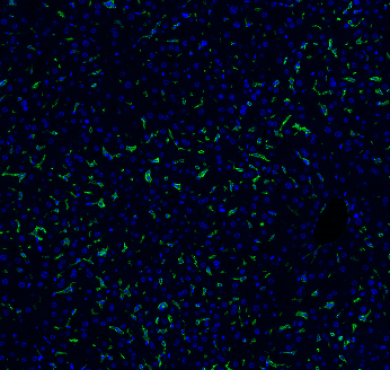
| Description | PCNA is a protein encoded by the PCNA gene which is approximately 28,7 kDa. PCNA is localised to the nucleus. It is involved in the telomere C-strand synthesis and trans-lesion synthesis. It is found in the nucleus and is a cofactor of DNA polymerase-delta. It acts as a homotrimer and helps increase the processivity of leading strand synthesis during DNA replication. In response to DNA damage, this protein is ubiquitinated and is involved in the RAD6-dependent DNA repair pathway. PCNA is expressed in the liver, lung, bone marrow, muscle and kidney. Mutations in the PCNA gene may result in ataxia-telangiectasia-like disorder. STJ96933 was developed from clone 12D10 and was affinity-purified from mouse ascites by affinity-chromatography using specific immunogen. This antibody detects endogenous PCNA protein. |
| Applications | IHC, WB |
| Dilution range | WB 1:5000 IHC 1:200 |
| Specificity | The antibody detects endogenous PCNA protein. |
| Protein Name | Proliferating cell nuclear antigen PCNA Cyclin |
| Immunogen | Synthetic Peptide |
| Immunogen Region | N-term |
| Storage Instruction | Store at -20°C, and avoid repeat freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Note | For Research Use Only (RUO). |
| Validated Application |
| Host | Mouse |
|---|---|
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Clone ID | 12D10 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Purification | The antibody was affinity-purified from mouse ascites by affinity-chromatography using specific immunogen. |
| Isotype | IgGMale |
| Formulation | Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide. |
| Gene ID | 5111 |
|---|---|
| Gene Symbol | PCNA |
| Database Links | HGNC:8729 OMIM:176740 |
| Alternative Names | Proliferating cell nuclear antigen PCNA Cyclin |
| Function | Auxiliary protein of DNA polymerase delta and is involved in the control of eukaryotic DNA replication by increasing the polymerase's processibility during elongation of the leading strand. Induces a robust stimulatory effect on the 3'-5' exonuclease and 3'-phosphodiesterase, but not apurinic-apyrimidinic (AP) endonuclease, APEX2 activities. Has to be loaded onto DNA in order to be able to stimulate APEX2. Plays a key role in DNA damage response (DDR) by being conveniently positioned at the replication fork to coordinate DNA replication with DNA repair and DNA damage tolerance pathways . Acts as a loading platform to recruit DDR proteins that allow completion of DNA replication after DNA damage and promote postreplication repair: Monoubiquitinated PCNA leads to recruitment of translesion (TLS) polymerases, while 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitination of PCNA is involved in error-free pathway and employs recombination mechanisms to synthesize across the lesion. |
| Post-translational Modifications | Phosphorylated. Phosphorylation at Tyr-211 by EGFR stabilizes chromatin-associated PCNA. Acetylated by CREBBP and p300/EP300; preferentially acetylated by CREBBP on Lys-80, Lys-13 and Lys-14 and on Lys-77 by p300/EP300 upon loading on chromatin in response to UV irradiation . Lysine acetylation disrupts association with chromatin, hence promoting PCNA ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation in response to UV damage in a CREBBP- and EP300-dependent manner . Acetylation disrupts interaction with NUDT15 and promotes degradation . Ubiquitinated . Following DNA damage, can be either monoubiquitinated to stimulate direct bypass of DNA lesions by specialized DNA polymerases or polyubiquitinated to promote recombination-dependent DNA synthesis across DNA lesions by template switching mechanisms. Following induction of replication stress, monoubiquitinated by the UBE2B-RAD18 complex on Lys-164, leading to recruit translesion (TLS) polymerases, which are able to synthesize across DNA lesions in a potentially error-prone manner. An error-free pathway also exists and requires non-canonical polyubiquitination on Lys-164 through 'Lys-63' linkage of ubiquitin moieties by the E2 complex UBE2N-UBE2V2 and the E3 ligases, HLTF, RNF8 and SHPRH. This error-free pathway, also known as template switching, employs recombination mechanisms to synthesize across the lesion, using as a template the undamaged, newly synthesized strand of the sister chromatid. Monoubiquitination at Lys-164 also takes place in undamaged proliferating cells, and is mediated by the DCX(DTL) complex, leading to enhance PCNA-dependent translesion DNA synthesis. Sumoylated during S phase. Methylated on glutamate residues by ARMT1/C6orf211. |
| Cellular Localization | Nucleus. Colocalizes with CREBBP, EP300 and POLD1 to sites of DNA damage . Forms nuclear foci representing sites of ongoing DNA replication and vary in morphology and number during S phase. Together with APEX2, is redistributed in discrete nuclear foci in presence of oxidative DNA damaging agents. |
| Swiss-Prot Key | P12004_HUMAN |
 Anti-PCNA antibody[STJ96933](图4)](/uploads/ueditor/20200825/1-200R515523T15.png)